NX1P2
NX-series NX1P2 CPU Units

Up to eight axes of control via EtherCAT
- Features
- Lineup
- Specifications
- Dimensions
- Catalog / Manual / CAD / Software
last update: December 1, 2023
Electrical and Mechanical Specifications
| Item | Specification | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | NX1P2-1[]40DT[] | NX1P2-9024DT[] | |
| Enclosure | Mounted in a panel | ||
| Dimensions (mm) *1 | 154 × 100 × 71 mm (W×H×D) | 130 × 100 × 71 mm (W×H×D) | |
| Weight *2 | NX1P2-1[]40DT: 650 g
NX1P2-1[]40DT1: 660 g |
NX1P2-9024DT: 590 g
NX1P2-9024DT1: 590 g |
|
| Unit power
supply |
Power supply voltage | 24 VDC (20.4 to 28.8 VDC) | |
| Unit power consumption *3 | NX1P2-1[]40DT: 7.05 W
NX1P2-1[]40DT1: 6.85 W |
NX1P2-9024DT: 6.70 W
NX1P2-9024DT1: 6.40 W |
|
| Inrush current *4 | For cold start at room temperature:
10 A max./0.1 ms max. and 2.5 A max./150 ms max. |
||
| Current capacity of power
supply terminal *5 |
4 A max. | ||
| Isolation method | No isolation: between the Unit power supply terminal and internal
circuit |
||
| Power supply
to the NX Unit power supply |
NX Unit power supply
capacity |
10 W max. | |
| NX Unit power supply
efficiency |
0.8 | ||
| Isolation method | No isolation: between the Unit power supply terminal and NX Unit
power supply |
||
| I/O Power Supply to NX Units | Not provided *6 | ||
| External
connection terminals |
Communication connector | RJ45 for EtherNet/IP Communications × 1
RJ45 for EtherCAT Communications × 1 |
|
| Screwless clamping terminal
block |
For Unit power supply input, grounding, and input signal: 1 (Removable)
For output signal: 1 (Removable) |
||
| Output terminal (service
supply) |
Not provided | ||
| RUN output terminal | Not provided | ||
| NX bus connector | 8 NX Units can be connected | ||
| Option board slot | 2 | 1 | |
*2. Includes the End Cover. The weight of the End Cover is 82 g.
*3. Includes the SD Memory Card and Option Board. The NX Unit power consumption to NX Units is not included.
*4. The inrush current may vary depending on the operating condition and other conditions. Therefore, select fuses,
breakers, and external power supply devices that have enough margin in characteristic and capacity, considering the
condition under which the devices are used.
*5. The amount of current that can be passed constantly through the terminal. Do no exceed this current value when you
use a through-wiring for the Unit power supply.
*6. When the type of the I/O power supply to NX Units you use is the supply from NX bus, an Additional I/O Power Supply
Unit is required. The maximum I/O power supply current from an Additional I/O Power Supply Unit is 4 A. Refer to the
NX-series NX1P2 CPU Unit Hardware User’s Manual (Cat. No. W578) for details.
General Specifications
| Item | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
| Enclosure | Mounted in a panel | |
| Grounding method | Ground to less than 100 Ω. | |
| Operating
environment |
Ambient operating
temperature |
0 to 55°C |
| Ambient operating
humidity |
10% to 95% (with no condensation) | |
| Atmosphere | Must be free from corrosive gases. | |
| Ambient storage
temperature |
-25 to 70°C (excluding battery) | |
| Altitude | 2,000 m max. | |
| Pollution degree | 2 or less: Meets IEC 61010-2-201. | |
| Noise immunity | 2 kV on power supply line (Conforms to IEC 61000-4-4.) | |
| Overvoltage
category |
Category II: Meets IEC 61010-2-201. | |
| EMC immunity
level |
Zone B | |
| Vibration
resistance |
Conforms to IEC 60068-2-6.
5 to 8.4 Hz with 3.5-mm amplitude, 8.4 to 150 Hz, acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 100 min each in X, Y, and Z directions (10 sweeps of 10 min each = 100 min total) |
|
| Shock resistance | Conforms to IEC 60068-2-27.
147 m/s2, 3 times in X, Y, and Z directions |
|
| Battery | Life | 5 years (Power ON time rate 0% (power OFF)) |
| Model | CJ1W-BAT01 (sold separately) | |
| Applicable standards *1 | cULus, EU, UKCA, RCM, KC, NK, LR | |
*1 Consult your OMRON representative for the most recent applicable standards for each model.
Performance Specifications
| Item | NX1P2- | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11[][][][]/
11[][][][]1 |
10[][][][]/
10[][][][]1 |
90[][][][]/
90[][][][]1 |
||||
| Processing
time |
Instruction
execution times |
LD instruction | 3.3 ns | |||
| Math instructions (for long
real data) |
70 ns or more | |||||
| Pro-
gramming |
Program
capacity *1 |
Size | 1.5 MB | |||
| Quantity | Number of POU
definitions |
450 | ||||
| Number of POU
Instances |
1,800 | |||||
| Memory
capacity for variables *2 |
Retain
attributes |
Size | 32 kB | |||
| Number of
variables |
5,000 | |||||
| No Retain
attributes |
Size | 2 MB | ||||
| Number of
variables |
90,000 | |||||
| Data types | Number of data types | 1,000 | ||||
| Memory for
CJ-series Units (Can be specified with AT specifica- tions for variables.) |
CIO Area | 0 to 6,144 channel (0 to 6,143) *3 | ||||
| Work Area | 0 to 512 channel (W0 to W511) *3 | |||||
| Holding Area | 0 to 1,536 channel (H0 to H1,535) *4 | |||||
| DM Area | 0 to 16,000 channel (D0 to F15,999) *4 | |||||
| EM Area | --- | |||||
| Motion
control |
Number of
controlled axes *5 |
Maximum number of
controlled axes |
12 axes | 10 axes | 4 axes | |
| Motion control
axes |
8 axes | 6 axes | --- | |||
| Single-axis
position control axes |
4 axes | 4 axes | 4 axes | |||
| Maximum number of used
real axes |
8 axes | 6 axes | 4 axes | |||
| Used motion
control servo axes |
4 axes | 2 axes | --- | |||
| Used single-
axis position control servo axes |
4 axes | 4 axes | 4 axes | |||
| Maximum number of axes
for linear interpolation axis control |
4 axes per axes group | --- | ||||
| Number of axes for circular
interpolation axis control |
2 axes per axes group | --- | ||||
| Maximum number of axes groups | 8 axes groups | --- | ||||
| Motion control period | Same as the period for primary periodic task | |||||
| Cams | Number of
cam data points |
Maximum points
per cam table |
65,535 points | --- | ||
| Maximum points
for all cam tables |
262,140 points | --- | ||||
| Maximum number of cam
tables |
80 tables | --- | ||||
| Position units | Pulse, mm, μm, nm, degree, and inch | |||||
| Override factors | 0.00% or 0.01% to 500.00% | |||||
| Built-in
EtherNet/IP port |
Number of ports | 1 | ||||
| Physical layer | 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX | |||||
| Frame length | 1,514 bytes max. | |||||
| Media access method | CSMA/CD | |||||
| Modulation | Baseband | |||||
| Topology | Star | |||||
| Baud rate | 100 Mbps/s (100BASE-TX) | |||||
| Transmission media | STP (shielded, twisted-pair) cable of Ethernet category 5,
5e or higher |
|||||
| Maximum transmission distance between
Ethernet switch and node |
100 m | |||||
| Maximum number of cascade
connections |
There are no restrictions if an Ethernet switch is used. | |||||
| CIP
service: Tag data links (cyclic communi- cations) |
Maximum number of
connections |
32 | ||||
| Packet interval *6 | Can be set for each connection.
2 to 10,000 ms in 1-ms increments |
|||||
| Permissible
communications band |
3,000 pps *7 (including heartbeat) | |||||
| Maximum number of tag
sets |
32 | |||||
| Tag types | Network variables
CIO/WR/HR/DM |
|||||
| Number of tags per con-
nection (i.e., per tag set) |
8 (7 tags if Controller status is included in the tag set.) | |||||
| Maximum number of tags | 256 | |||||
| Maximum link data size per
node (total size for all tags) |
19,200 bytes | |||||
| Maximum data size per
connection |
600 bytes | |||||
| Maximum number of
registrable tag sets |
32
(1 connection = 1 tag set) |
|||||
| Maximum tag set size | 600 bytes
(Two bytes are used if Controller status is included in the tag set.) |
|||||
| Multi-cast packet filter *8 | Supported. | |||||
| CIP
message service: Explicit messages |
Class 3 (number of
connections) |
32
(clients plus server) |
||||
| UCMM
(non- connec- tion type) |
Maximum
number of clients that can communicate at one time |
32 | ||||
| Maximum
number of servers that can communicate at one time |
32 | |||||
| Number of TCP sockets | 30 | |||||
| Secure
Socket Service |
Maximum number of
Secure Socket |
30 | ||||
| TLS Version | 1.2 | |||||
| Built-in
EtherCAT port |
Communications standard | IEC 61158 Type12 | ||||
| EtherCAT master specifications | Class B (Feature Pack Motion Control compliant) | |||||
| Physical layer | 100BASE-TX | |||||
| Modulation | Baseband | |||||
| Baud rate | 100 Mbps (100BASE-TX) | |||||
| Duplex mode | Auto | |||||
| Topology | Line, daisy chain, branching and ring *9 | |||||
| Transmission media | Twisted-pair cable of category 5 or higher
(double-shielded straight cable with aluminum tape and braiding) |
|||||
| Maximum transmission distance between
nodes |
100 m | |||||
| Maximum number of slaves | 16 | |||||
| Range of node addresses that can be set | 1 to 192 | |||||
| Maximum process data size | Input: 1,434 bytes
Output: 1,434 bytes *10 |
|||||
| Maximum process data size per slave | Input: 1,434 bytes
Output: 1,434 bytes |
|||||
| Communications cycle | 2,000 μs to 8,000 μs in 250-μs increments | |||||
| Sync jitter | 1 μs max. | |||||
| Serial
Communi- cations (Serial Communi- cations Option Board) |
Communications method | half duplex | ||||
| Synchronization | Start-stop | |||||
| Baud rate | 1.2/2.4/4.8/9.6/19.2/38.4/57.6/115.2 kbps | |||||
| Transmission distance | Depends on Option Board. | |||||
| Supported protocol | Host link, Modbus-RTU master, and no-protocol | |||||
| Unit con-
figuration |
Maximum
number of connectable Units |
Maximum number of NX
Units that can be mounted to the CPU Unit |
8 | |||
| Maximum number of NX
Units for entire controller |
24
On CPU Rack: 8 On EtherCAT Slave Terminals: 16 |
|||||
| Power
supply |
Model | A non-isolated power supply for DC input is built into the
CPU Unit. |
||||
| Power OFF detection time | 2 to 8 ms | |||||
| Option
Board |
Number of slots | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Built-in I/O | Input | Number of points | 24 | 24 | 14 | |
| Output | Number of points | 16 | 16 | 10 | ||
| Load short-circuit
protection |
11[][]DT/10[][]DT/9024DT: Not provided (NPN)
11[][]DT1/10[][]DT1/9024DT1: Provided (PNP) |
|||||
| Internal
clock |
Accuracy | At ambient temperature of 55°C: -3.5 to 0.5 min error
per month At ambient temperature of 25°C: -1.5 to 1.5 min error per month At ambient temperature of 0°C: -3 to 1 min error per month |
||||
| Retention time of built-in capacitor | At ambient temperature of 40°C: 10 days | |||||
*2. Memory used for CJ-series Units is included.
*3. The value can be set in 1 ch increments. The value is included in the total size of variables without a Retain attribute.
*4. The value can be set in 1 ch increments. The value is included in the total size of variables with a Retain attribute.
*5. Refer to the NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Motion Control User’s Manual (Cat. No. W507) for the description of this term.
*6. Data will be refreshed at the set interval, regardless of the number of nodes.
*7. "pps" means packets per second, i.e., the number of communications packets that can be sent or received in one
second.
*8. As the EtherNet/IP port implements the IGMP client, unnecessary multi-cast packets can be filtered by using an
Ethernet switch that supports IGMP Snooping.
*9. Ring topology is supported with the project version 1.40 or later.
Slaves on a ring topology should support a ring topology. If Omron slaves, please see the user's manual of slaves.
*10.For project unit version earlier than 1.40, the data must be within one frame.
Function Specifications
| Item | NX1P2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tasks | Function | I/O refresh and the user program are executed in units
that are called tasks. Tasks are used to specify execution conditions and execution priority. |
||
| Periodi-
cally Executed Tasks |
Maximum Number
of Primary Periodic Tasks |
1 | ||
| Maximum Number
of Periodic Tasks |
2 | |||
| Condi-
tionally Executed Tasks |
Maximum Number
of Event Tasks |
32 | ||
| Execution
Condition |
When Activate Event Task instruction is executed or
when condition expression for variable is met |
|||
| Setup | System Service Monitoring
Settings |
Not supported | ||
| Pro-
gramming |
POUs
(program- organization units) |
Programs | POUs that are assigned to tasks. | |
| Function Blocks | POUs that are used to create objects with specific
conditions. |
|||
| Functions | POUs that are used to create an object that determine
unique outputs for the inputs, such as for data processing. |
|||
| Programming
Languages |
Types | Ladder diagrams * and structured text (ST) | ||
| Namespaces | Namespaces are used to create named groups of POU
definitions. |
|||
| Variables | External
Access of variables |
Network
Variables |
The function which allows access from the HMI, host
computers, or other Controllers |
|
| Data Types | Data types | Boolean | BOOL | |
| Bit Strings | BYTE, WORD, DWORD, LWORD | |||
| Integers | INT, SINT, DINT, LINT, UINT, USINT, UDINT, ULINT | |||
| Real Numbers | REAL and LREAL | |||
| Durations | TIME | |||
| Dates | DATE | |||
| Times of Day | TIME_OF_DAY | |||
| Date and Time | DATE_AND_TIME | |||
| Text Strings | STRING | |||
| Derivative Data Types | Structures, Unions, and Enumerations | |||
| Structures | Function | A derivative data type that groups together data with
different data types. |
||
| Maximum Number
of Members |
2048 | |||
| Nesting Maximum
Levels |
8 | |||
| Member Data
Types |
Basic data types, structures, unions, enumerations,
array variables |
|||
| Specifying
Member Offsets |
You can use member offsets to place structure
members at any memory locations. |
|||
| Union | Function | A derivative data type that enables access to the same
data with different data types. |
||
| Maximum Number
of Members |
4 | |||
| Member Data
Types |
BOOL, BYTE, WORD, DWORD, and LWORD | |||
| Enumer-
ation |
Function | A derivative data type that uses text strings called
enumerators to express variable values. |
||
| Data Type
Attributes |
Array
Specifica- tions |
Function | An array is a group of elements with the same data
type. You specify the number (subscript) of the element from the first element to specify the element. |
|
| Maximum Number
of Dimensions |
3 | |||
| Maximum Number
of Elements |
65535 | |||
| Array
Specifications for FB Instances |
Supported | |||
| Range Specifications | You can specify a range for a data type in advance.
The data type can take only values that are in the specified range. |
|||
| Libraries | You can use user libraries. | |||
| Motion
Control |
Control Modes | Position control, Velocity control, and Torque control | ||
| Axis Types | Servo axes, Virtual servo axes, Encoder axes, and
Virtual encoder axes |
|||
| Positions that can be managed | Command positions and actual positions | |||
| Single Axes | Single-Axis
Position Control |
Absolute
Positioning |
Positioning is performed for a target position that is
specified with an absolute value. |
|
| Relative
Positioning |
Positioning is performed for a specified travel distance
from the command current position. |
|||
| Interrupt Feeding | Positioning is performed for a specified travel distance
from the position where an interrupt input was received from an external input. |
|||
| Cyclic
Synchronous Absolute Positioning |
A positioning command is output each control period
in Position Control Mode. |
|||
| Single-axis
Velocity Control |
Velocity Control | Velocity control is performed in Position Control
Mode. |
||
| Cyclic
Synchronous Velocity Control |
A velocity command is output each control period in
Velocity Control Mode. |
|||
| Single-axis
Torque Control |
Torque Control | The torque of the motor is controlled. | ||
| Single-axis
Synchro- nized Control |
Starting Cam
Operation |
A cam motion is performed using the specified cam
table. |
||
| Ending Cam
Operation |
The cam motion for the axis that is specified with the
input parameter is ended. |
|||
| Starting Gear
Operation |
A gear motion with the specified gear ratio is
performed between a master axis and slave axis. |
|||
| Positioning Gear
Operation |
A gear motion with the specified gear ratio and sync
position is performed between a master axis and slave axis. |
|||
| Ending Gear
Operation |
The specified gear motion or positioning gear motion is
ended. |
|||
| Synchronous
Positioning |
Positioning is performed in sync with a specified
master axis. |
|||
| Master Axis
Phase Shift |
The phase of a master axis in synchronized control is
shifted. |
|||
| Combining Axes | The command positions of two axes are added or
subtracted and the result is output as the command position. |
|||
| Single-axis
Manual Operation |
Powering the
Servo |
The Servo in the Servo Drive is turned ON to enable
axis motion. |
||
| Jogging | An axis is jogged at a specified target velocity. | |||
| Auxiliary
Functions for Single- axis Control |
Resetting Axis
Errors |
Axes errors are cleared. | ||
| Homing | A motor is operated and the limit signals, home
proximity signal, and home signal are used to define home. |
|||
| Homing with
specified parameters |
The parameters are specified, the motor is operated,
and the limit signals, home proximity signal, and home signal are used to define home. |
|||
| High-speed
Homing Stopping |
Positioning is performed for an absolute target position
of 0 to return to home. An axis is decelerated to a stop. |
|||
| Immediately
Stopping |
An axis is stopped immediately. | |||
| Setting Override
Factors |
The target velocity of an axis can be changed. | |||
| Changing the
Current Position |
The command current position or actual current
position of an axis can be changed to any position. |
|||
| Enabling External
Latches |
The position of an axis is recorded when a trigger
occurs. |
|||
| Disabling
External Latches |
The current latch is disabled. | |||
| Zone Monitoring | You can monitor the command position or actual
position of an axis to see when it is within a specified range (zone). |
|||
| Enabling Digital
Cam Switches |
You can turn a digital output ON and OFF according to
the position of an axis |
|||
| Monitoring Axis
Following Error |
You can monitor whether the difference between the
command positions or actual positions of two specified axes exceeds a threshold value. |
|||
| Resetting the
Following Error |
The error between the command current position and
actual current position is set to 0. |
|||
| Torque Limit | The torque control function of the Servo Drive can be
enabled or disabled and the torque limits can be set to control the output torque. |
|||
| Slave Axis
Position Compensation |
This function compensates the position of the slave
axis currently in synchronized control. |
|||
| Cam monitor | Outputs the specified offset position for the slave axis
in synchronous control. |
|||
| Start Velocity | You can set the initial velocity when axis motion starts. | |||
| Axes Groups | Multi-axes
Coordi- nated Control |
Absolute Linear
Interpolation |
Linear interpolation is performed to a specified
absolute position. |
|
| Relative Linear
Interpolation |
Linear interpolation is performed to a specified relative
position. |
|||
| Circular 2D
Interpolation |
Circular interpolation is performed for two axes. | |||
| Axes Group
Cyclic Synchronous Absolute Positioning |
A positioning command is output each control period in
Position Control Mode. |
|||
| Auxiliary
Functions for Multi- axes Coordi- nated Control |
Resetting Axes
Group Errors |
Axes group errors and axis errors are cleared. | ||
| Enabling Axes
Groups |
Motion of an axes group is enabled. | |||
| Disabling Axes
Groups |
Motion of an axes group is disabled. | |||
| Stopping Axes
Groups |
All axes in interpolated motion are decelerated to a
stop. |
|||
| Immediately
Stopping Axes Groups |
All axes in interpolated motion are stopped immediately. | |||
| Setting Axes
Group Override Factors |
The blended target velocity is changed during
interpolated motion. |
|||
| Reading Axes
Group Positions |
The command current positions and actual current
positions of an axes group can be read. |
|||
| Changing the
Axes in an Axes Group |
The Composition Axes parameter in the axes group
parameters can be overwritten temporarily. |
|||
| Common
Items |
Cams | Setting Cam
Table Properties |
The end point index of the cam table that is specified
in the input parameter is changed. |
|
| Saving Cam
Tables |
The cam table that is specified with the input
parameter is saved in nonvolatile memory in the CPU Unit. |
|||
| Generating Cam
Tables |
The cam table is generated from the cam property and
cam node that is specified in input parameters. |
|||
| Parameters | Writing MC
Settings |
Some of the axis parameters or axes group parameters
are overwritten temporarily. |
||
| Changing Axis
Parameters |
You can access and change the axis parameters from
the user program. |
|||
| Auxiliary
Functions |
Count Modes | You can select either Linear Mode (finite length) or
Rotary Mode (infinite length). |
||
| Unit Conversions | You can set the display unit for each axis according to
the machine. |
|||
| Acceler-
ation/ Decelera- tion Control |
Automatic
Acceleration/ Deceleration Control |
Jerk is set for the acceleration/deceleration curve for
an axis motion or axes group motion. |
||
| Changing the
Acceleration and Deceleration Rates |
You can change the acceleration or deceleration rate
even during acceleration or deceleration. |
|||
| In-Position Check | You can set an in-position range and in-position check
time to confirm when positioning is completed. |
|||
| Stop Method | You can set the stop method to the immediate stop
input signal or limit input signal. |
|||
| Re-execution of Motion
Control Instructions |
You can change the input variables for a motion
control instruction during execution and execute the instruction again to change the target values during operation. |
|||
| Multi-execution of Motion
Control Instructions (Buffer Mode) |
You can specify when to start execution and how to
connect the velocities between operations when another motion control instruction is executed during operation. |
|||
| Continuous Axes Group
Motions (Transition Mode) |
You can specify the Transition Mode for multi-
execution of instructions for axes group operation. |
|||
| Monitoring
Functions |
Software limits | The movement range of an axis is monitored. | ||
| Following Error | The error between the command current value and the
actual current value is monitored for each axis. |
|||
| Velocity,
Acceleration Rate, Deceleration Rate, Torque, Interpolation Velocity, Interpolation Acceleration Rate, and Interpolation Dceleration Rate |
You can set and monitor warning values for each axis
and each axes group. |
|||
| Absolute Encoder Support | You can use an OMRON 1S-series Servomotor or G5-
series Servomotor with an Absolute Encoder to eliminate the need to perform homing at startup. |
|||
| Input Signal Logic Inversion | You can inverse the logic of immediate stop input
signal, positive limit input signal, negative limit input signal, or home proximity input signal. |
|||
| External Interface Signals | The Servo Drive input signals listed on the right are
used. Home signal, home proximity signal, positive limit signal, negative limit signal, immediate stop signal, and interrupt input signal |
|||
| Unit (I/O)
Man- agement |
EtherCAT
slaves |
Maximum Number of Slaves | 16 | |
| CJ-Series
Units |
Maximum Number of Units | Not supported | ||
| Communi-
cations |
Peripheral USB Port | Not supported | ||
| Built-in
EtherNet/IP Port |
Communications Protocol | TCP/IP and UDP/IP | ||
| CIP Com-
munica- tions Service |
Tag Dta Links | Programless cyclic data exchange is performed with
the devices on the EtherNet/IP network. |
||
| Message
Communications |
CIP commands are sent to or received from the
devices on the EtherNet/IP network. |
|||
| TCP/IP
Applica- tions |
Socket Services | Data is sent to and received from any node on
Ethernet using the UDP or TCP protocol. Socket communications instructions are used. |
||
| Secure Socket
service (Client) |
Establishes a TLS session with the TCP protocol,
and sends and receives arbitrary data to and from the server and any node on the Ethernet using instructions for secure socket communication. |
|||
| FTP Client | Files are transferred via FTP from the CPU Unit to
computers or Controllers at other Ethernet nodes. FTP client communications instructions are used. |
|||
| FTP Server | Files can be read from or written to the SD Memory
Card in the CPU Unit from computers at other Ethernet nodes. |
|||
| Automatic Clock
Adjustment |
Clock information is read from the NTP server at the
specified time or at a specified interval after the power supply to the CPU Unit is turned ON. The internal clock time in the CPU Unit is updated with the read time. |
|||
| SNMP Agent | Built-in EtherNet/IP port internal status information is
provided to network management software that uses an SNMP manager. |
|||
| EtherCAT
Port |
Supported
Services |
Process Data
Communications |
A communications method to exchange control
information in cyclic communications between the EtherCAT master and slaves. This communications method is defined by CoE. |
|
| SDO
Communications |
A communications method to exchange control
information in noncyclic event communications between EtherCAT master and slaves. This communications method is defined by CoE. |
|||
| Network Scanning | Information is read from connected slave devices and
the slave configuration is automatically generated. |
|||
| DC (Distributed Clock) | Time is synchronized by sharing the EtherCAT system
time among all EtherCAT devices (including the master). |
|||
| Enable/Disable Settings for
Slaves |
The slaves can be enabled or disabled as
communications targets. |
|||
| Disconnecting/Connecting
Slaves |
Temporarily disconnects a slave from the EtherCAT
network for maintenance, such as for replacement of the slave, and then connects the slave again. |
|||
| Supported
Application Protocol |
CoE | SDO messages of the CAN application can be sent to
slaves via EtherCAT |
||
| Serial Com-
munication |
Protocol | Host link (FINS), no-protocol, and Modbus-RTU master
(when connected to the Serial Communications Option Board) |
||
| Communications Instructions | FTP client instructions, CIP communications
instructions, socket communications instructions, SDO message instructions, noprotocol communications instructions, and Modbus RTU protocol instructions |
|||
| Operation
Man- agement |
RUN Output Contacts | Not supported | ||
| System
Man- agement |
Event Logs | Function | Events are recorded in the logs | |
| Maximum
Number of Events |
System Event Log | 576 *2 | ||
| Access Event Log | 528 *3 | |||
| User-defined Event Log | 512 | |||
| Debugging | Online
Editing |
Single | Programs, function blocks, functions, and global
variables can be changed online. More than one operators can change POUs individually via network. |
|
| Forced Refreshing | The user can force specific variables to TRUE or
FALSE. |
|||
| Maximum
Number of Forced Variables |
Device Variables
for EtherCAT Slaves |
64 | ||
| Device Variables
for CJ-series Units and Variables with AT Specifications |
Not supported | |||
| MC Test Run | Motor operation and wiring can be checked from the
Sysmac Studio. |
|||
| Synchronizing | The project file in the Sysmac Studio and the data in
the CPU Unit can be made the same when online. |
|||
| Differentiation Monitoring | You can monitor when a variable changes to TRUE or
changes to FALSE. |
|||
| Maximum Number of Contacts | 8 | |||
| Data Tracing | Types | Single Triggered
Trace |
When the trigger condition is met, the specified number
of samples are taken and then tracing stops automatically. |
|
| Continuous
Trace |
Data tracing is executed continuously and the trace
data is collected by the Sysmac Studio. |
|||
| Maximum Number of
Simultaneous Data Traces |
2 | |||
| Maximum Number of Records | 10000 | |||
| Maximum Number of Sampled
Variables |
48 variables | |||
| Timing of Sampling | Sampling is performed for the specified task period, at
the specified time, or when a sampling instruction is executed. |
|||
| Triggered Traces | Trigger conditions are set to record data before and
after an event. |
|||
| Trigger
Conditions |
When BOOL variable changes to TRUE or FALSE
Comparison of non-BOOL variable with a constant Comparison Method: Equals (=), Greater than (>), Greater than or equals (≥), Less Than (<), Less than or equals (≤), Not equal (≠) |
|||
| Delay | Trigger position setting: A slider is used to set the
percentage of sampling before and after the trigger condition is met. |
|||
| Simulation | The operation of the CPU Unit is emulated in the
Sysmac Studio. |
|||
| Reliability
functions |
Self-
Diagnosis |
Controller
Errors |
Levels | Major faults, partial faults, minor faults, observation,
and information |
| Maximum number
of message languages |
9 (Sysmac Studio)
2 (NS-series PT) |
|||
| User-
defined Errors |
Function | User-defined errors are registered in advance and then
records are created by executing instructions. |
||
| Levels | 8 | |||
| Maximum number
of message languages |
9 | |||
| Security | Protecting
Software Assets and Preventing Operating Mistakes |
CPU Unit Names and Serial IDs | When going online to a CPU Unit from the Sysmac
Studio, the CPU Unit name in the project is compared to the name of the CPU Unit being connected to. |
|
| Protection | User Program
Transfer with no Restoration Information |
You can prevent reading data in the CPU Unit from the
Sysmac Studio. |
||
| CPU Unit Write
Protection |
You can prevent writing data to the CPU Unit from the
Sysmac Studio or SD Memory Card. |
|||
| Overall Project
File Protection |
You can use passwords to protect .smc files from
unauthorized opening on the Sysmac Studio. |
|||
| Data Protection | You can use passwords to protect POUs on the
Sysmac Studio. |
|||
| Verification of Operation
Authority |
Online operations can be restricted by operation rights
to prevent damage to equipment or injuries that may be caused by operating mistakes. |
|||
| Number of
Groups |
5 | |||
| Verification of User Program
Execution ID |
The user program cannot be executed without entering
a user program execution ID from the Sysmac Studio for the specific hardware (CPU Unit). |
|||
| SD
Memory Card functions |
Storage Type | SD Memory Card,
SDHC Memory Card |
||
| Application | Automatic Transfer from SD
Memory Card |
When the power supply to the Controller is turned ON,
the data that is stored in the autoload directory of the SD Memory Card is transferred to the Controller. |
||
| Program transfer from SD
Memory Card |
With the specification of the system-defined variable,
you can transfer a program that is stored in the SD Memory Card to the Controller. |
|||
| SD Memory Card Operation
Instructions |
You can access SD Memory Cards from instructions in
the user program. |
|||
| File Operations from the
Sysmac Studio |
You can perform file operations for Controller files in
the SD Memory Card and read/write general-purpose document files on the computer. |
|||
| SD Memory Card Life
Expiration Detection |
Notification of the expiration of the life of the SD
Memory Card is provided in a system-defined variable and event log. |
|||
| Backing
up data |
SD Memory
Card backups |
Operating
methods |
CPU Unit front
panel DIP switch |
Backup, verification, and restoration operations are
performed by manipulating the front-panel DIP switch on the CPU Unit. |
| Specification
with system- defined variables |
Backup, verification, and restoration operations are
performed by manipulating system-defined variables.*4 |
|||
| SD Memory Card
Window in Sysmac Studio |
Backup and verification operations are performed from
the SD Memory Card Window of the Sysmac Studio. |
|||
| Special
instruction |
The special instruction is used to backup data. | |||
| Protection | Disabling backups
to SD Memory Cards |
Backing up data to a SD Memory Card is prohibited. | ||
| Sysmac Studio Controller backups | The Sysmac Studio is used to backup, restore, or
verify Controller data. |
|||
*1. Inline ST is supported. (Inline ST is ST that is written as an element in a ladder diagram.)
*2. This is the total of 512 events for the CPU Unit and 64 events for the NX Unit.
*3. This is the total of 512 events for the CPU Unit and 16 events for the NX Unit.
*4. Restore is supported with unit version 1.14 or later.
Input Terminal Block
Terminal Arrangement
The description is given for each CPU Unit model.
NX1P2-1[]40DT[]
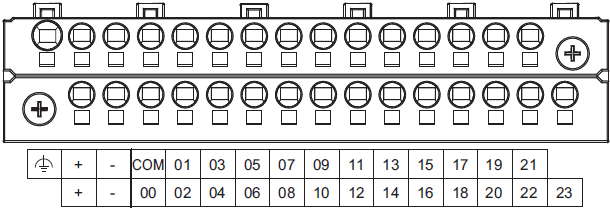
| Symbol | Terminal name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Functional ground terminal | The functional ground terminal. Connect
the ground wire to the terminal. |
Refer to the NX-series NX1P2
CPU Unit Hardware User's Manual (Cat. No. W578) for details. |
| +/- | Unit power supply terminals | These terminals are connected to the Unit
power supply. The + terminals and - terminals are internally connected to each other. |
|
| COM | Common terminal | Common terminal for the input circuits | Refer to the Input Specifications. |
| 00 to 15 | Input terminals | General-purpose input A | |
| 16 to 23 | Input terminals | General-purpose input B |
NX1P2-9024DT[]
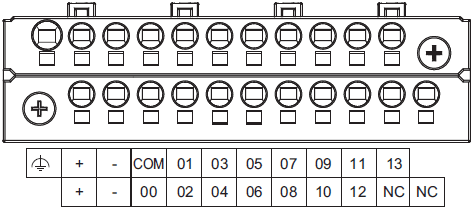
| Symbol | Terminal name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Functional ground terminal | The functional ground terminal. Connect
the ground wire to the terminal. |
Refer to the NX-series NX1P2
CPU Unit Hardware User's Manual (Cat. No. W578) for details. |
| +/- | Unit power supply terminals | These terminals are connected to the Unit
power supply. The + terminals and - terminals are internally connected to each other. |
|
| COM | Common terminal | Common terminal for the input circuits | Refer to the Input Specifications. |
| 00 to 13 | Input terminals | General-purpose input A | |
| NC | NC | Do not connect anything. | --- |
Input Specifications
The specifications depends on the input terminal numbers of the model. *1
| Item | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
| Input type | General-purpose input A | General-purpose input B |
| Input terminal number | NX1P2-1[]40DT[]: 00 to 15
NX1P2-9024DT[]: 00 to 13 |
NX1P2-1[]40DT[]: 16 to 23
NX1P2-9024DT[]: None |
| Internal I/O common | For both NPN/PNP | |
| Input voltage | 24 VDC (15 to 28.8 VDC) | |
| Connected sensor | Two-wire or three-wire sensors | |
| Input impedance | --- | 4.3 kΩ |
| Input current | 4.22 mA | 5.3 mA typical |
| ON voltage | 15 VDC min. | |
| OFF voltage/current | 5 VDC max./1 mA max. | |
| ON response time *2 | 2.5 µs max. | 1 ms max. |
| OFF response time *2 | 2.5 µs max. | 1 ms max. |
| ON/OFF filter time *3 | No filter, 0.25 ms, 0.5 ms, 1 ms (default), 2 ms, 4 ms, 8 ms, 16 ms, 32 ms, 64 ms, 128 ms,
256 ms |
|
| Circuit configuration | 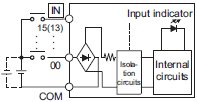 |
 |
*1. The following specifications apply to models with lot number 18321M (products produced in March 2021) or earlier.
| Item | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
| Input type | General-purpose input A | General-purpose input B |
| Input terminal number | NX1P2-1[]40DT[]: 00 to 15
NX1P2-9024DT[]: 00 to 13 |
NX1P2-1[]40DT[]: 16 to 23
NX1P2-9024DT[]: None |
| Internal I/O common | For both NPN/PNP | |
| Input voltage | 24 VDC (15 to 28.8 VDC) | |
| Connected sensor | Two-wire or three-wire sensors | |
| Input impedance | 4.0 kΩ | 4.3 kΩ |
| Input current | 5.8 mA typical | 5.3 mA typical |
| ON voltage | 15 VDC min. | |
| OFF voltage/current | 5 VDC max./1 mA max. | |
| ON response time *2 | 2.5 µs max. | 1 ms max. |
| OFF response time *2 | 2.5 µs max. | 1 ms max. |
| ON/OFF filter time *3 | No filter, 0.25 ms, 0.5 ms, 1 ms (default), 2 ms, 4 ms, 8 ms, 16 ms, 32 ms, 64 ms, 128 ms,
256 ms |
|
| Circuit configuration | 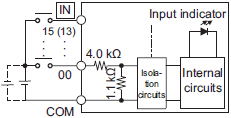 |
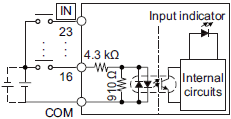 |
on the Support Software is added to these values.
*3. Set the filter time for every 4 points.
Output Terminal Block
Terminal Arrangement
The description is given for each CPU Unit model.
NX1P2-1[]40DT
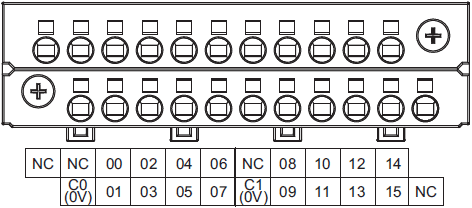
| Symbol | Terminal name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 (0V),
C1 (0V) |
Common terminal | Connected to the 0-V side of the I/O power supply.
C0 (0V) and C1 (0V) are independent from each other inside the CPU Unit. |
Refer to the Output Specifications. |
| 00 to 15 | Output terminals | NPN (sinking) type output | |
| NC | NC | Do not connect anything. | --- |
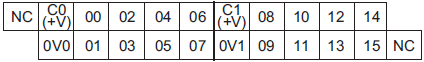
NX1P2-1[]40DT1
The appearance of the terminal block is the same as NX1P2-1[]40DT.
| Symbol | Terminal name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 (+V),
C1 (+V) |
Common terminal | Connected to the 24-V side of the I/O power supply.
C0 (+V) and C1 (+V) are independent from each other inside the CPU Unit. |
Refer to the Output Specifications. |
| 0V0, 0V1 | 0 V terminal | Supplies 0 V for the internal circuits for driving.
0V0 and 0V1 are independent from each other inside the CPU Unit. |
|
| 00 to 15 | Output terminals | PNP (sourcing) type output with the load short-
circuit protection function |
|
| NC | NC | Do not connect anything. | --- |
NX1P2-9024DT
The appearance of the terminal block is the same as NX1P2-1[]40DT.
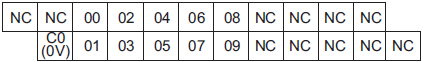
| Symbol | Terminal name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 (0V) | Common terminal | Connected to the 0-V side of the I/O power supply. | Refer to the Output Specifications. |
| 00 to 09 | Output terminals | NPN (sinking) type output | |
| NC | NC | Do not connect anything. | --- |
NX1P2-9024DT1
The appearance of the terminal block is the same as NX1P2-1[]40DT.
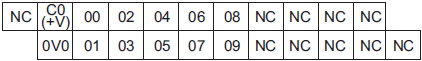
| Symbol | Terminal name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 (+V) | Common terminal | Connected to the 24-V side of the I/O power supply. | Refer to the Output Specifications. |
| 0V0 | 0 V terminal | Supplies 0 V for the internal circuits for driving. | |
| 00 to 09 | Output terminals | PNP (sourcing) type output with the load short-
circuit protection function |
|
| NC | NC | Do not connect anything. | --- |
Output Specifications
The models of the CPU Units are divided according to the following two output types: the NPN (sinking) type and PNP (sourcing) type.
There is no difference in specifications between the models with different output terminal numbers.
| Item | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
| NX1P2-[][][][]DT | NX1P2-[][][][]DT1 | |
| Internal I/O common | NPN (sinking) | PNP (sourcing) |
| Maximum switching capacity | 12 to 24 VDC (10.2 to 28.8 VDC), 300 mA
per point |
24 VDC (15 to 28.8 VDC), 300 mA per
point |
| NX1P2-1[]40DT[]: 1.8 A/common (3.6 A/Unit)
NX1P2-9024DT[]: 2.4 A/common (2.4 A/Unit) |
||
| Minimum switching capacity | 12 to 24 VDC (10.2 to 28.8 VDC), 1 mA | 24 VDC (15 to 28.8 VDC), 1 mA |
| Leakage current | 0.1 mA max. | |
| Residual voltage | 1.5 V max. | |
| ON response time | 0.1 ms max. | 0.5 ms max. |
| OFF response time | 0.8 ms max. | 1.0 ms max. |
| Current consumption from
I/O power supply *1 |
--- | NX1P2-1[]40DT1: 40 mA/common
NX1P2-9024DT1: 50 mA/common |
| Load short-circuit protection | Not provided | Provided *2 |
| Circuit configuration | NX1P2-1[]40DT
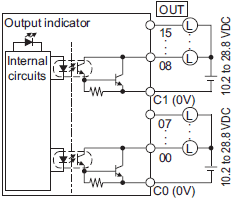 |
NX1P2-1[]40DT1
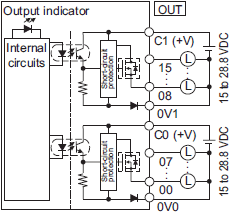 |
NX1P2-9024DT
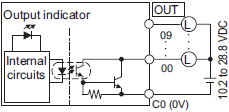 |
NX1P2-9024DT1
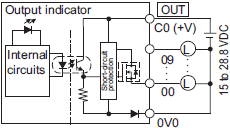 |
|
0Vn terminal. The current consumption of any external load is excluded.
*2. The load short-circuit protection is provided for each point of the PNP (sourcing) type output terminal. It protects the
output circuits when a load short circuit occurs.
Part Names and Functions
CPU Unit
The following two models have the different numbers of the option board slots and built-in I/O points, but the names and functions of their parts are the same. Refer to the Ordering Information page for the CPU Unit models and specifications such as the number of built-in I/O points.
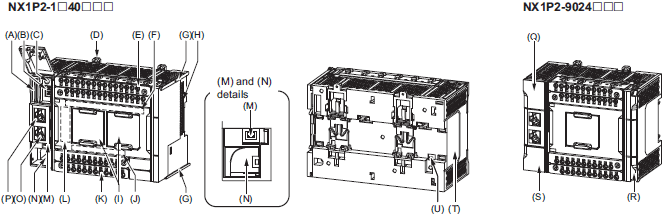
| Letter | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| A | SD Memory Card connector | Connects the SD Memory Card to the CPU Unit. |
| B | DIP switch | Used in Safe Mode *1 or when backing up data *2. Normally, turn OFF all of
the pins. |
| C | SD Memory Card power supply
switch |
Turns OFF the power supply so that you can remove the SD Memory Card. |
| D | DIN Track mounting hook | These hooks are used to mount the Unit to a DIN Track. |
| E | Input terminal block | This terminal block is used for wiring for the Unit power supply, grounding,
and built-in input. |
| F | Input indicator | Shows the operation status of the built-in input. |
| G | Unit hookup guides | These guides are used to mount an NX Unit or End Cover. |
| H | NX bus connector | This connector is used to connect the CPU Unit to the NX Unit on the
right of the CPU Unit. |
| I | Option board slot 1 (left),
Option board slot 2 (right) |
Remove the covers of the slots and mount Option Boards. For the models
with 24 built-in I/O points, only one slot is provided. Keep the removed covers in a safe place. |
| J | Output indicator | Shows the operation status of the built-in output. |
| K | Output terminal block | This terminal block is used to wire the built-in output. |
| L | CPU Unit operation status indicator | Shows the operation status of the CPU Unit. |
| M | Battery connector | Connector to mount the backup battery that is sold separately. |
| N | Battery slot | Used to mount the backup battery that is sold separately. |
| O | Built-in EtherCAT port (port 2) | Connects the built-in EtherCAT with an Ethernet cable. |
| P | Built-in EtherNet/IP port (port 1) | Connects the built-in EtherNet/IP with an Ethernet cable. |
| Q | SD Memory Card cover | Cover for the SD Memory Card and DIP switch. The cover swings upward. |
| R | End Cover | Cover to protect the CPU Unit and NX Units.
One End Cover is provided with the CPU Unit. |
| S | Battery cover | Cover for the battery slot. Remove this cover when you mount/remove
the battery. |
| T | ID information indication | Shows the ID information of the CPU Unit. |
| U | DIN Track contact plate | This plate is connected internally to the functional ground terminal on the
terminal block. |
*1. To use Safe Mode, set the DIP switch as shown below and then turn ON the power supply to the Controller.
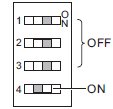
mode. Use the Safe Mode if you do not want to execute the user program when the power supply is turned ON or if it
is difficult to connect the Sysmac Studio.
For information on Safe Mode, refer to the NJ/NX-series Troubleshooting Manual (Cat. No. W503).
*2. Refer to the NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Software User’s Manual (Cat. No. W501) for details on backing up data.
Option Board
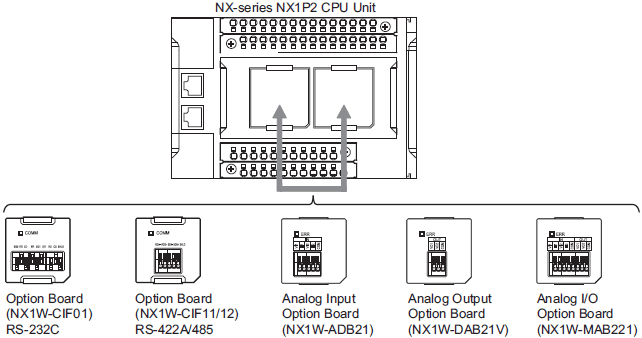
Specifications of Serial Communications Option Board
| Item | Specification | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | NX1W-CIF01 | NX1W-CIF11 | NX1W-CIF12 |
| Communications port | One RS-232C port | One RS-422A/485 port | One RS-422A/485 port
(isolated) |
| Communications method | Half-duplex | ||
| Synchronization method | Start-stop synchronization | ||
| Baud rate | 1.2/2.4/4.8/9.6/19.2/38.4/57.6/115.2 kbps | ||
| Transmission distance | 15 m | 50 m | 500 m |
| Supported protocol | Host link, Modbus-RTU master, and no-protocol | ||
| Connection type | Screwless clamping terminal
block (9 terminals) |
Screwless clamping terminal block (5 terminals) | |
| Applicable wire size | AWG28 to 20 | AWG24 to 20 | |
| Dimensions (mm) *1 | 35.9 × 35.9 × 13.5 (W×H×D) | ||
| Weight | 16 g | 13 g | 14 g |
| Power consumption | Included in the CPU Unit power consumption.
The Option Board power consumption is included in the definition of the CPU Unit power consumption. |
||
| Isolation method | No isolation | Isolation *2 | |
protrudes through the CPU Unit surface. Refer to the NX-series NX1P2 CPU Unit Hardware User’s Manual (Cat. No.
W578) for details.
*2. The terminals are isolated from the internal circuits of the CPU Unit.
RS-232C Option Board (NX1W-CIF01)
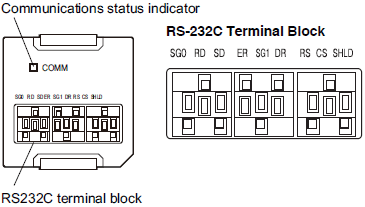
| Abbreviation | Signal name | I/O |
|---|---|---|
| SG0 | Signal grounding | --- |
| RD | Receive data | Input |
| SD | Send data | Output |
| ER | Data terminal ready | Output |
| SG1 | Signal grounding | --- |
| DR | Data set ready | Input |
| RS | Send request | Output |
| CS | Data can be sent | Input |
| SHLD | Shield | --- |
such as an CJ1W-CIF11 and NT-AL001, or an NV3W-M[]20L Programmable Terminal.
2. The terminal block is not removable.
RS-422A/485 Option Board (NX1W-CIF11/NX1W-CIF12)
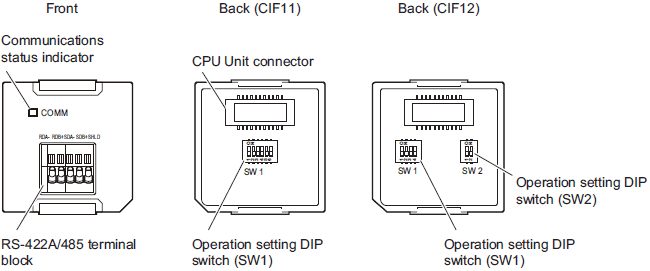
Use a narrow-tipped tool such as a flat-blade screwdriver to change the settings of the DIP switches.
RS-422A/485 Terminal Block
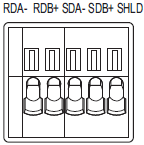
| Abbreviation | Four-wire type selected | Two-wire type selected | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal name | I/O | Signal name | I/O | |
| RDA- | Reception data - | Input | Communication data - | I/O * |
| RDB+ | Reception data + | Communication data + | ||
| SDA- | Transmission data - | Output | Communication data - | I/O * |
| SDB+ | Transmission data + | Communication data + | ||
| SHLD | Shield | |||
* For two-wire connection, either the RDA-/RDB+ pair or SDA-/SDB+ pair can be used.
Specifications of Analog I/O Option Board
| Item | Specification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | NX1W-ADB21 | NX1W-DAB21V | NX1W-MAB221 | ||||
| I/O | Analog input | Analog output | Analog I/O | ||||
| Voltage input | 0 to 10 V | 2 words total | --- | 0 to 10 V | 2 words total | ||
| Current input | 0 to 20 mA | --- | 0 to 20 mA | ||||
| Voltage output | --- | 0 to 10 V | 2 words | 0 to 10 V | 2 words | ||
| Connection type | Screwless clamping terminal
block (5 terminals) |
Screwless clamping terminal
block (3 terminals) |
Screwless clamping terminal
block (8 terminals) |
||||
| Applicable wire size | AWG24 to 20 | ||||||
| Dimensions (mm) * | 35.9 × 35.9 × 28.2 (W×H×D) | ||||||
| Weight | 24 g | 24 g | 26 g | ||||
| Power consumption | Included in the CPU Unit power consumption.
The Option Board power consumption is included in the definition of the CPU Unit power consumption. |
||||||
| Isolation method | No isolation | ||||||
through the CPU Unit surface. Refer to the NX-series NX1P2 CPU Unit Hardware User's Manual (Cat. No. W578) for details.
Analog Input Option Board (NX1W-ADB21)
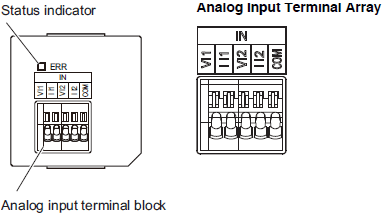
| Abbreviation | Signal name |
|---|---|
| V I1 | Voltage input 1 |
| I I1 | Current input 1 |
| V I2 | Voltage input 2 |
| I I2 | Current input 2 |
| COM | Input common |
Note: When you use the current input, be sure to short-circuit V I1 with I I1, and short-circuit V I2 with I I2.
Analog Input Specifications
| Item | Specification | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage input | Current input | ||
| Input method | Single-ended input | Single-ended input | |
| Input range | 0 to 10 V | 0 to 20 mA | |
| Input conversion range | 0 to 10.24 V | 0 to 30 mA | |
| Absolute maximum rating | -1 to 15 V | -4 to 30 mA | |
| Input impedance | 200 kΩ min. | Approx. 250 Ω | |
| Resolution | 1/4,000 (full scale) | 1/2,000 (full scale) | |
| Overall accuracy | 25°C | ±0.5% (full scale) | ±0.6% (full scale) |
| 0 to 55°C | ±1.0% (full scale) | ±1.2% (full scale) | |
| Averaging processing | Not provided | ||
| Conversion time | Internal sampling time: 2 ms per point * | ||
refresh time.
Analog Output Option Board (NX1W-DAB21V)
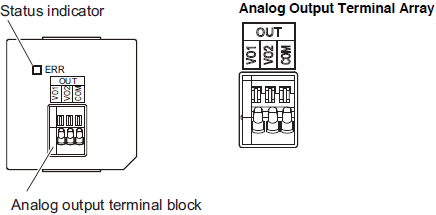
| Abbreviation | Signal name |
|---|---|
| VO1 | Voltage output 1 |
| VO2 | Voltage output 1 |
| COM | Output common |
Analog Output Specifications
| Item | Specification | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage output | Current output | ||
| Output range | 0 to 10 V | --- | |
| Output conversion range | 0 to 10.24 V | --- | |
| Allowable load resistance | 2 kΩ min. | --- | |
| Output impedance | 0.5 Ω max. | --- | |
| Resolution | 1/4,000 (full scale: 4,000) | --- | |
| Overall accuracy | 25°C | ±0.5% (full scale) | --- |
| 0 to 55°C | ±1.0% (full scale) | --- | |
| Conversion time | Internal sampling time: 2 ms per point * | ||
refresh time.
Analog I/O Option Board (NX1W-MAB221)
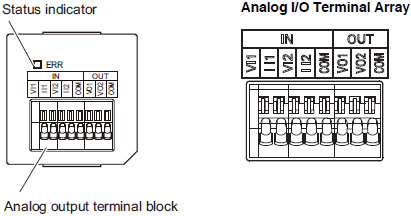
| Abbreviation | Signal name | |
|---|---|---|
| IN | VI1 | Voltage output 1 |
| II1 | Current input 1 | |
| VI2 | Voltage input 2 | |
| II2 | Current input 2 | |
| COM | Input common | |
| OUT | VO1 | Voltage output 1 |
| VO2 | Voltage output 2 | |
| COM | Output common | |
Note: When you use the current input, be sure to short-circuit VI1 with II1, and short-circuit VI2 with II2.
Analog I/O Specifications
| Item | Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage I/O | Current I/O | |||
| Analog
input section |
Input method | Single-ended input | Single-ended input | |
| Input range | 0 to 10 V | 0 to 20 mA | ||
| Input conversion range | 0 to 10.24 V | 0 to 30 mA | ||
| Absolute maximum rating | -1 to 15 V | -4 to 30 mA | ||
| Input impedance | 200 kΩ min. | Approx. 250 Ω | ||
| Resolution | 1/4,000 (full scale) | 1/2,000 (full scale) | ||
| Overall accuracy | 25°C | ±0.5% (full scale) | ±0.6% (full scale) | |
| 0 to 55°C | ±1.0% (full scale) | ±1.2% (full scale) | ||
| Averaging processing | Not provided | |||
| Analog
output section |
Output range | 0 to 10 V | --- | |
| Output conversion range | 0 to 10.24 V | --- | ||
| Allowable load resistance | 2 kΩ min. | --- | ||
| Output impedance | 0.5 Ω max. | --- | ||
| Resolution | 1/4,000 (full scale) | --- | ||
| Overall accuracy | 25°C | ±0.5% (full scale) | --- | |
| 0 to 55°C | ±1.0% (full scale) | --- | ||
| Conversion time | Internal conversion time: 6 ms (Total of 4 channels) * | |||
refresh time.
last update: December 1, 2023


